Is milk allowed on the keto diet? What about dairy products on the keto diet? What should you avoid?
In this article, learn more about the nutrients and carbohydrates in milk, the best keto-friendly dairy products with low carbs, and how the keto diet can help with lactose intolerance.

It is very likely that you grew up with milk and often drank milk as a child. In fact, most newborn mammals depend on their mother’s milk and sufficient nutrients for survival.
While mammals have always been biologically capable of producing milk, domestication of certain animals did not begin until around 10,000 BC – which led to an increase in milk consumption.
But can we drink milk on a keto diet?
Classic cow milk is unfortunately not keto-friendly. However, good news for cheese lovers: you can eat dairy products with a ketogenic diet.
Not only is it a delicious snack, cheese can also be the extra source of fat you need to reach your daily macros. First, a few words of caution when it comes to dairy products in a ketogenic diet.
In this article we will discuss everything you need to know about dairy and ketosis, including the best low carb options for dairy products you can eat and which you should avoid.
Milk and Keto Diet
What Exactly is Milk?
The oldest evidence of domesticated dairy cows comes from Turkestan (8 000 years BC) and Greece (6 500 years BC).
In ancient Egypt, milk was only intended for the most affluent people. Cows and sheep were sacred and their milk production made them valued possessions.
The first pasteurization tests were carried out in 1862 by Louis Pasteur, a microbiologist, who developed a procedure to ensure the safety of milk and made it possible to distribute and store milk after it had left the farm.
This white liquid from the udder of a cow is incredibly versatile and has been one of the most processed and sought-after foods for years.
To meet this high global demand, it is quite common to find antibiotics and hormones in certain types of milk, which are used to ward off disease and increase milk production.
It is therefore important to choose your milk and dairy products carefully to ensure that you get the best quality.
Grass-fed dairy cows are the cows from which you should get your milk. These cows are fed only natural feed and are kept in a pleasant and appropriate environment.
Milk is the core substance of all dairy products, from butter to cheese, from whipped cream to buttermilk.
Milk is 87% water and 13% solid components, including proteins such as caesin, minerals such as phosphorus and calcium, as well as fats and vitamins such as B2 and B12. Milk provides some important nutrients.
However, milk naturally contains sugar–lactose. Lactose consists of glucose and galactose. Lactase is an enzyme in our bodies that break down lactose into its individual components. Glucose is obtained and released into the blood stream. Galactose is simply converted into Glucose and then used the same way.
How many carbohydrates does milk have?
There are different types of milk, whole milk, buttermilk, skim milk and different amounts of low-fat milk.
The different types of milk vary in fat content with a slight variation in carbohydrates and protein.
If the fat in the milk is reduced, the carbohydrates in the milk are increased.
Less Fat = More Carbs
Classic cow’s milk is generally considered unsuitable for the keto diet. Some low-carb followers still consume it, but you really shouldn’t if your goal is to get into ketosis.
Carbohydrate content per 240 ml (cow) milk (one glass):
- 3.5% whole milk = 12g carbohydrates, 8g fat, 8g protein
- 1.5% milk = 13g carbohydrates, 2.5g fat, 8g protein
- Skimmed milk = 13g carbohydrates, 0g fat, 8g protein
As you can see, the carbohydrates in milk are too high for the keto diet. Therefore, it is recommended not to drink milk with the ketogenic diet, because otherwise you will very quickly exceed your daily carbohydrate limit of 25-50 g of carbohydrates and thus prevent ketosis.
However, there are different types of milk substitutes out there that we will discuss in this post.

Effects of Milk
Lactase is a slow enzyme. The conversion of galactose to glucose slows down the complete breakdown of lactose, which means it takes longer to completely enter the bloodstream. Because of this, blood sugar level rise slightly slower than would be the case with conventional table sugar. However, increases in blood sugar and insulin levels can be avoided, by simply avoiding milk.
Additionally, some people do not produce lactase or not enough of it, which means that they can not really breakdown and use lactose properly. This is what causes digestive problem. Even if you are not lactose intolerant, overly consuming dairy products may cause you some discomfort.
Relieve Lactose Intolerance Symptoms
Lactose is a sugar found in milk.
It is also one of the ingredients that is difficult to digest in dairy products, which is what leads to lactose intolerance in some people.
Symptoms include flatulence, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, and nausea.
If you have often experienced these symptoms while eating dairy products, there are a few strategies you can try.
1. Stick to hard and long-aged dairy products. These products are much lower in lactose content and should be easy on the digestive tract.
2. Use ghee. Ghee is an ideal alternative for those who are sensitive to dairy products because the milk solids have been removed. Swap butter for ghee in all your meals.
Try these first two tips before moving on to the next two options.
3. Make sure you’re not dealing with casein sensitivity. Lactose has the worst reputation, but casein could also be a cause of your upset stomach. So if you only exclude lactose, you will continue to experience the same unpleasant symptoms of casein sensitivity.
This is how you can tell the difference between lactose intolerance and casein sensitivity:
You experience the same gastrointestinal disorders with casein as with lactose, but you can also suffer an allergic reaction when it comes to casein intolerance.
Hives, itching, wheezing, anaphylaxis and facial flushing, which should not be taken lightly, are indicators of casein intolerance.
If you suspect a casein allergy or intolerance, it is best to have it checked before trying any of the keto dairy products in this article.
In the end you may find that your best option is this one:
4. No dairy products whatsoever. You don’t need dairy products for a ketogenic diet to work. And if it’s something that’s not good for you, it may be time to remove it from your life.
For people in this category, coconut or nut alternatives can be a helpful solution.
There are a few milk alternatives listed below, which are fine so long as you choose the unsweetened versions!
So how does the keto diet relieve lactose intolerance symptoms?
Often the problem is actually carbohydrates, not milk.
Once you have eliminated and drastically reduced most of the carbohydrates in your diet, you won’t be as affected by the small amount of lactose you eat in cheese or whipped cream.
Another helpful tip is to stick with high-fat cheese, as it naturally contains less lactose.
Good Milk Alternatives
There are a few milk substitutes suitable for the keto diet:
- Almond milk
- Soy milk
- Coconut milk
Almond milk, with its slightly nutty flavor, is great for exceptionally low carbohydrate content. It has less than 1g of sugar and about 3g of fat per 100ml, this is the best alternative to traditional cow’s milk. The nutrients found in almond milk are also interesting. Some included are iron and vitamin E. Almond milk is often fortified with calcium.
Soy milk has a similar carbohydrate content compared to almond milk, but has a lower fat content with 2g of fat per 100ml of soy milk.

However, the protein content of soy milk is about 3.3g/100ml more than almond milk.
Coconut milk is another nice alternative to cow’s milk. It is characterized by its very high fat content–a whopping 21g per 100ml. That makes coconut milk a great source of energy. The fatty acids found in the coconut milk are medium-chain triglycerides, which have proven to be good for rapidly available energy. Nevertheless, you should pay attention to the carbohydrates. On average, coconut milk contains 6g carbohydrates per 100ml, 3g of which is sugar. Also, be aware that due to the much higher fat content, coconut milk contains significantly more calories than almond milk or soy milk.
Additionally, you should be sure to buy the unsweetened version of milk substitute.
Bad Milk Alternatives
There are other milk alternatives, however they may not necessarily be the best for the keto diet. Some of these are:
- Oat milk
- Rice milk
- Lupine milk
- Lactose-free milk
Oat milk, rice milk, and lupine milk all contain more than 6g of carbohydrates per 100ml on average. They are richer in carbs than conventional cow’s milk! Therefore, they are no good alternative.
Even lactose-free milk is not a better option, because even if it is lactose-free, it still contains as much sugar as before it was made to be lactose-free. The difference is that lactose has already been broken down using lactase. Remember, milk-related digestive problems are related to those who do not produce lactase or not enough of it to breakdown lactose properly. So, lactace-free milk is really just milk where the lactace is already broken down for the recipient–their body must not do that now. Even after this processing, the individual components, glucose and galactose, are still present. This shortens the digestive process and the sugar gets into the blood even faster than with untreated milk.
Dairy and Keto Diet
As mentioned, dairy products are suitable for the keto diet.
First, it is important to understand that not all dairy products are the same.
- Some dairy products are rich in carbohydrates, while others contain a very good low carb and protein-fat combination that you need to stay in ketosis.
- If your chosen dairy products contain too many net carbohydrates, it will be more difficult for you to meet your daily macronutrient goals to stay below 20-30g net carbohydrates.
- Consuming dairy products can also be difficult for some people to digest. You may experience unwanted side effects and health problems such as upset stomach, bloating, sinus problems, acne and joint pain if your body cannot digest them properly.
- If you consume pasteurized milk instead of raw milk, you won’t get all the good bacteria that can help you digest dairy products more easily.
Even if certain dairy products are keto friendly, if you notice any of these symptoms, dairy products may not be right for you.
Another reason to be cautious about dairy products is the simple fact that highly processed foods can quickly make you eat too much of them.
While dairy products can be useful in small quantities, there is still a risk of ruining your calorie and macro goals in just one small meal.
To keep your overall milk consumption within keto diet limits, we should first go over a few basic rules…
- To get the full benefit of dairy products in a ketogenic diet, you should opt for organic quality (why this is important, more on this later), natural, full-fat varieties instead of low-fat or artificial flavors.
- As you will see in the next section, 1% and 2% fat dairy products are actually filled with carbohydrates. As the fat is removed and sugar is added, you are left with two things you definitely don’t want in a keto diet.
- Just because you have the green light for certain dairy products in Keto doesn’t mean that you should eat dairy products here all the time. A ketogenic diet emphasizes whole foods and natural foods. Dairy products are processed foods and you should only enjoy them in small quantities.
- Remember: while dairy products are rich in proteins and fats, they are also very high in calories. A single portion of cheese can be about 100 calories on average.
- Be prepared for the extra protein boost.
- If you combine dairy products with another high-protein source, you may risk exceeding your macros if you are not careful.
The 7 Best Keto Dairy Products
1. Butter
Organic butter from grazing cows is one of the best foods in the dairy products category. Butter is an excellent source of healthy fat with about 12g of fat and 0g of carbohydrates in just one tablespoon.

If weight loss is your goal, the only reason to limit your butter consumption is because of the calories. One tablespoon of butter contains around 100 calories.
The next option on our list goes one step further…
2. Ghee
Ghee is clarified butter. This means that the butter has been boiled longer to remove the water and milk solids. The remaining mixture is pure butterfat and ideal for a ketogenic diet.
It has 2g more fat than butter and only an additional 25 calories (and 0 g carbohydrates) per tablespoon.
Unlike butter, ghee is also easy to make yourself. Just buy a high-quality butter made from pasture milk and melt it slowly in a pot.
Ghee has another additional benefit compared to butter: 25% more short- and medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs). In comparison, butter has only 12-15%.
These types of fats are easily digestible and available faster as an energy source in your body, which means that you can get into ketosis faster with medium-chain triglycerides or MCT oil.
3. Whipped Cream, 30% fat
If you have made the switch from sugary lattes to keto coffee (or are in the process of doing so), you are probably experiencing some problems or withdrawal symptoms from sugar.
One way to make a keto-safe and sugar-free latte is to use whipped cream in your coffee.
Simply whip some whipped cream until stiff (you can also add a little vanilla extract and carbohydrate-free sweetener), then add a tablespoon to your coffee and drink your homemade keto latte.
Whipped cream can also be used in spicy recipes, such as a keto breakfast casserole with bacon, egg and cheese, or in keto dessert recipes to add an extra layer.
The next few dairy products also have the same creamy quality…
4. Fermented Yogurt, Greek Yogurt, and Kefir
If you think of fermentation, you probably associate this process with a lot of sugar. After all, sugar is what feeds the bacteria or the yeast.
And since sugar is not keto friendly, you may think that fermented foods are taboo. This is only partially true.
Yogurt and other sour milk products are based on lactic acid fermentation. When food is fermented, the microorganisms of bacteria or yeasts feed on the sugary carbohydrates.
This helps to eliminate the bad bacteria while leaving the good ones intact (probiotic benefits).
So while a large amount of sugar can be used to produce a fermented food, most of it has already been consumed by the bacteria.
In some cases, such as an unaromatic kombucha, less than 3g of carbohydrates and 1g of sugar remain per serving, making it an ideal option for a ketogenic diet.
However, this has one major caveat.
Care should be taken with most yogurts and fermented drinks such as kombucha and kefir. Many varieties on the market are fortified with unnecessary added sugar, making it more difficult to find a good ketogenic option. You must always pay attention to the list of ingredients and check the carbohydrate and sugar content in the nutritional information.
Pay attention to natural, full-fat yogurt, and kefir (without fruit pieces!).
Whenever it is a “low-fat” product where the fat is removed, such as 1% or 2% varieties, you can bet that added sugar will take its place.
And exactly the same applies to natural, full-fat Greek yogurt. There are good Greek yogurts that do not have too much sugar per portion and contain 18g of protein and 10g of fat. This can be quite a challenge if your grocery store has a very limited selection, but our next keto-suitable milk option is quite common…
5. Sour Cream
Sour cream tastes similar to Greek yogurt, but full-fat sour cream has almost no carbohydrates, so it is actually a much better option.
Sour cream is made by fermenting normal cream with certain types of lactic acid bacteria.
You probably don’t want to eat a bowl of raspberries, nuts and sour cream for breakfast, but some sour cream provides a creamy consistency that is perfect for dips, thickening sauces and as a carbohydrate-free ingredient for soups, for example.
Our last two milk options are probably what you have been waiting for…
Cheese lovers are delighted: there are many keto-friendly cheeses with low carbohydrate content to choose from.
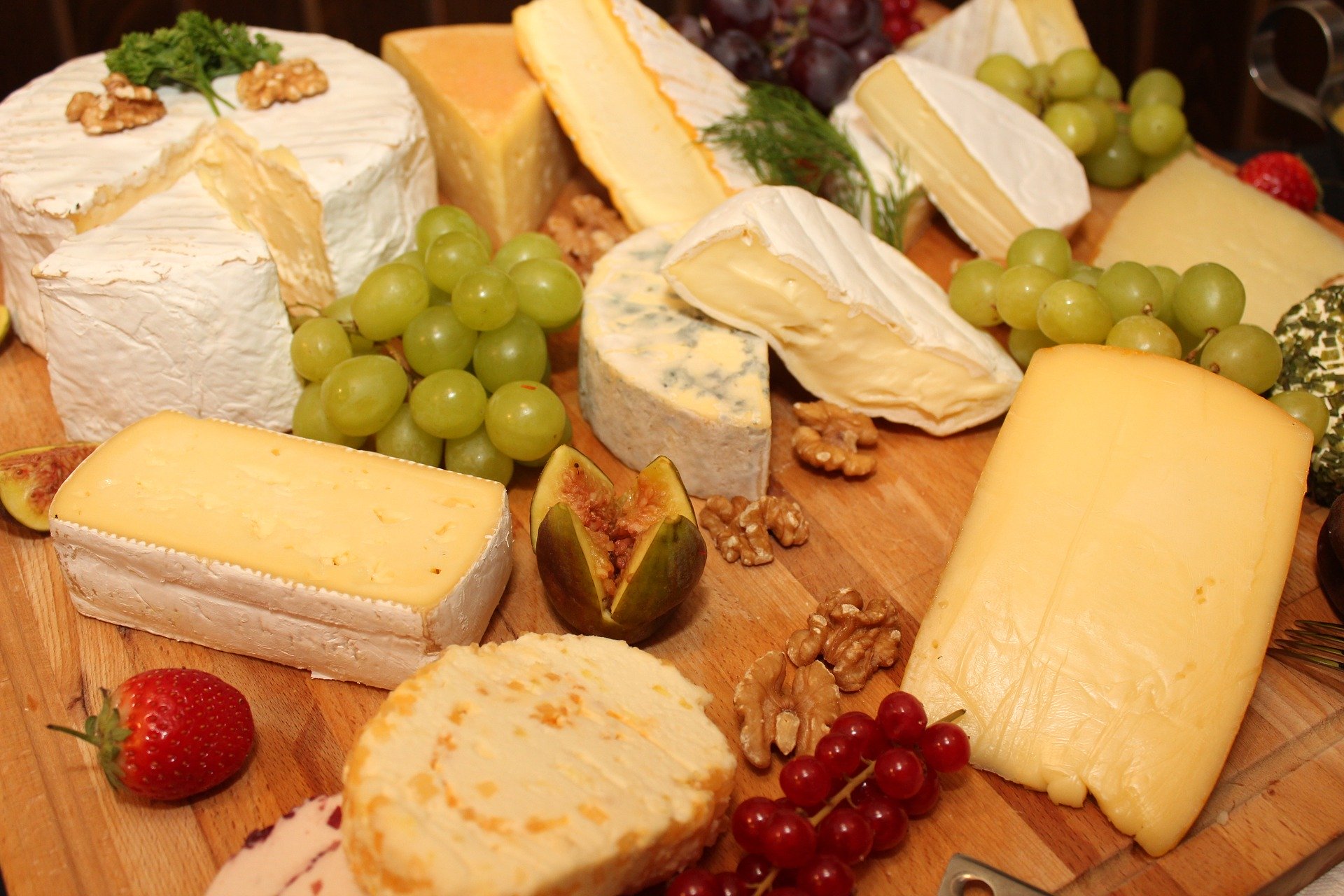

6. Hard Cheese
While some cheeses are taboo, most have very few carbohydrates and provide healthy fats.
A tip for choosing the right cheese is to look for longer matured options (e.g. blue cheese, Gouda or Parmesan cheese) as their carbohydrate content is lower.
This added benefit is due to the same bacteria-eating process that occurs in fermented yogurt and other foods.
Many hard or mature cheeses, such as Swiss cheese, Cheddar and Provolone, are also among the keto-friendly cheeses with lower carbohydrate content.
There are even some soft cheeses that you can prepare as a snack or add to your recipes…
7. Soft Cheese
Mozzarella, Brie, Münster, and Monterey Jack are all perfect cheeses, all of which contain very little carbohydrate and add variety to your ketogenic diet.
Cream cheese, cottage cheese, mascarpone and crème fraiche are other good options that you can eat as they are or add to your dishes for a creamier, richer taste.
Want some more about the details?
Here is the nutritional info for a 30g serving (usually 1 slice or stick) of some cheeses:
| Portion of: | Carbohydrates | Protein | Fat | KCal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swiss Cheese | .403g | 7.55g | 8.68g | 110 |
| Parmesan | .913g | 10.1g | 7.09g | 111 |
| Blue Cheese | .663g | 6.07g | 8.15g | 100 |
| Cheddar Cheese | 0.876g | 6.48g | 9.44g | 115 |
| Gouda | 0.629g | 7.07g | 7.78g | 101 |
| Provolone | 0.607g | 7.25g | 7.55g | 99.5 |
| Mozzarella | 1.58g | 6.73g | 5.61g | 83.6 |
| Brie | .128g | 5.88g | 7.85g | 94.7 |
These seven dairy products will help you to stay in ketosis in an intelligent way.
But knowing which dairy products to avoid will help you when you first start a ketogenic diet.
The 3 Worst Keto Dairy Products
1. Milk
As discussed above, low fat, reduced fat, 1.5% and 2% milk are all just clever names for the fact that the fat has been removed from the milk and additional sugars and carbohydrates have been added to improve the taste.
So, what about full-fat, goat or untreated raw milk on a keto diet?
In the case of goat’s milk, you only get 8.7g of protein for 10.9g of carbohydrates (ouch!) and 168 calories in a 230ml glass.
While untreated cow’s milk has beneficial bacteria, it also provides a proud 9.6 g of carbohydrates, as well as 6.6 g of protein and 134 calories per 200 ml.
As for whole milk, one glass provides 12.8 g of carbohydrates, 7.9 g of protein, and 146 calories.
Most types of milk consist mainly of water and sugar (plus a few other nutrients), so milk is not recommended for keto, as it contains too many carbohydrates and by drinking milk the daily macro goals can be quickly exceeded.
You are better advised to stick to low-carb cheese options that provide the same or better amounts of protein.
So, just try removing milk from your diet if you want to get into ketosis quickly and your ketogenic diet should be successful.
While you don’t need to completely remove the next dairy product from your diet, you should still take great care not to consume this food too often…
2. Creamer & Half and Half
Coffee cream or Half and Half is a milk product that is mainly used to whiten coffee or tea.
This milk product, boiled in the laboratory, consists of half milk, half cream. The different stages are achieved by mixing skimmed milk and the appropriate amount of sweet cream. It is pasteurized (ultra-high temperature treated) in order to have a longer shelf life.
What you really get is a mixture of sugar with a reduction in fat, two things you don’t want in a ketogenic diet.
Depending on the brand, this product can add up to 2 grams of extra carbohydrates per teaspoon to your keto macros!
Instead of using coffee cream or a half and half mix of milk and cream, choose high-fat whipped cream for your coffee or keto recipes to keep net carbohydrates low.
The same advice applies to the next dairy product…
3. Condensed/Evaporated Milk
Although most people do not drink condensed milk every day, condensed milk should not be added to your recipes if you want to stay in ketosis.
Condensed or evaporated condensed milk is made from milk by reducing the water content by boiling it over a long period of time.
The original manufacturing process involves adding up to 45% sugar after the actual condensation process, resulting in the very viscous sweetened condensed milk.
These super dense, compressed versions of milk syrup are nothing more than sugar water.
If a recipe requires one of these types of milk or condensed milk, be sure to omit it.
Exchange this unhealthy milk for an unsweetened coconut milk with the same thick consistency (thanks to healthy fats) without the extra sugar.
Conclusion
Enjoy dairy products during a keto diet (but in moderation). Milk is not the best option for the keto diet.
As long as you enjoy dairy products in moderation, choose the right sources, monitor your carbohydrate intake and include the extra amount in your daily macro and calorie goals, you can enjoy dairy products in a keto diet.
Try to buy organic and natural varieties. Conventional dairy products are loaded with harmful hormones, bacteria and antibiotics that put a strain on your system.
And if dairy products are not your thing or you are lactose intolerant, you can also opt for non-dairy alternatives. Organic dairy products are an excellent source of omega-3 anti-inflammatory fatty acids and CLA or conjugated linoleic acid, an omega-6 fatty acid that can help promote weight loss and increase muscle strength.
Follow these simple guidelines and you’ll never have to worry about your milk obsession ruining your keto experience again.
Thanks for reading!
Anna
www.readyforketo.com